Background Worthy Mars Photos
mclewis_13
Published
08/14/2014
Beautiful images from Mars, these are desktop worthy.
- List View
- Player View
- Grid View
Advertisement
-
1.
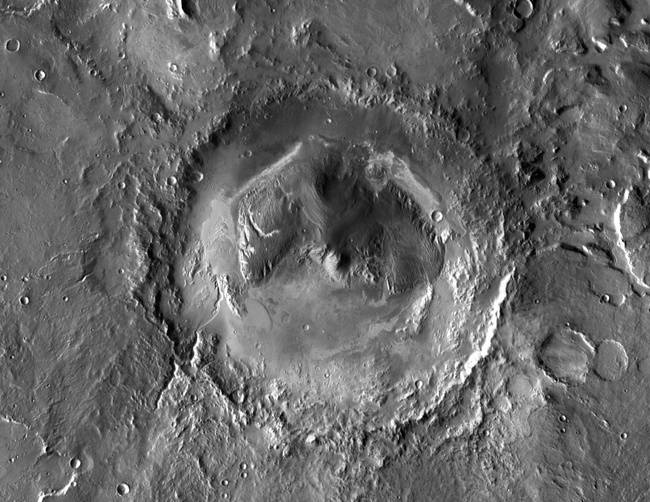 Gale is a crater on Mars near the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle at 5.4S 137.8E.2 It is 154 km 96 mi in diameter1 and estimated to be about 3.5-3.8 billion years old.
Gale is a crater on Mars near the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle at 5.4S 137.8E.2 It is 154 km 96 mi in diameter1 and estimated to be about 3.5-3.8 billion years old. -
2.
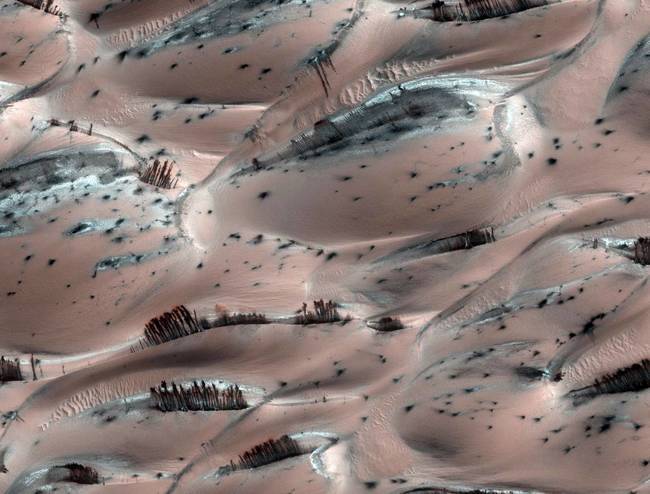 Naturally erupting dust clouds on Mars are creating structures that look surprisingly like trees near the planet's north pole. But don't be fooled ? it's just an optical illusion, NASA scientists say.The Martian "trees" are actually dark basaltic sand pushed to the surface of sand dunes by sun-heated solid carbon dioxide ice, or dry ice, sublimating directly into vapor, explained Candy Hansen, a member of NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO team at the University of Arizona.
Naturally erupting dust clouds on Mars are creating structures that look surprisingly like trees near the planet's north pole. But don't be fooled ? it's just an optical illusion, NASA scientists say.The Martian "trees" are actually dark basaltic sand pushed to the surface of sand dunes by sun-heated solid carbon dioxide ice, or dry ice, sublimating directly into vapor, explained Candy Hansen, a member of NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO team at the University of Arizona. -
3.
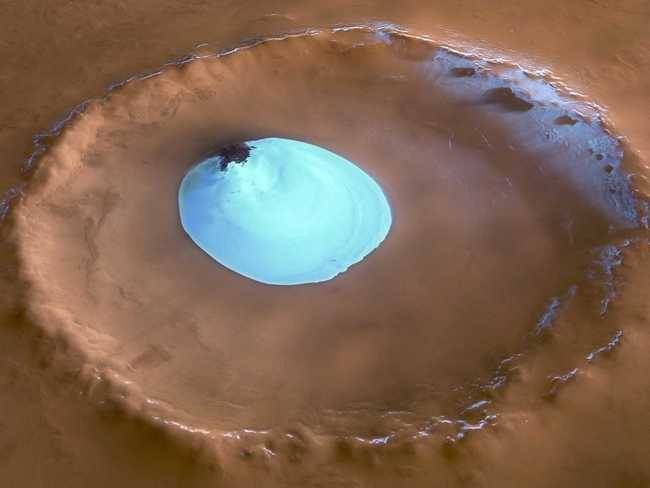 The above photo from the European Space Agency's Mars Express mission was taken on Feb 2, 2005. It shows a sheet of residual water ice in the crater. The crater is in the far northern latitudes of Mars.
The above photo from the European Space Agency's Mars Express mission was taken on Feb 2, 2005. It shows a sheet of residual water ice in the crater. The crater is in the far northern latitudes of Mars. -
4.
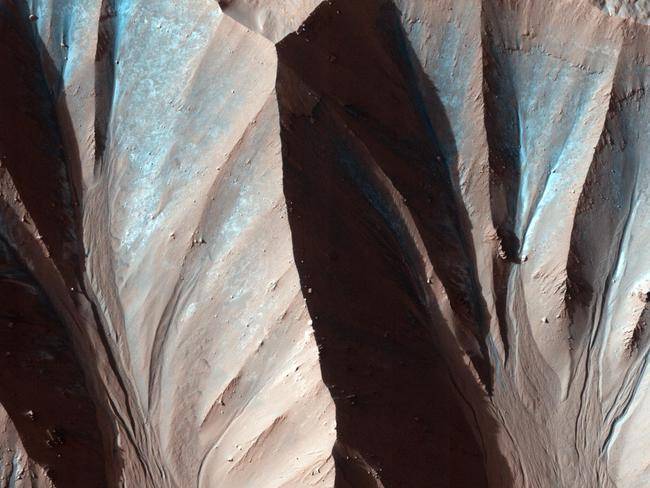 This image was taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE flying onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter mission.Gully landforms like those in this image are found in many craters in the mid-latitudes of Mars. Changes in gullies were first seen in images from the Mars Orbiter Camera in 2006, and studying such activity has been a high priority for HiRISE. Many examples of new deposits in gullies are now known.
This image was taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE flying onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter mission.Gully landforms like those in this image are found in many craters in the mid-latitudes of Mars. Changes in gullies were first seen in images from the Mars Orbiter Camera in 2006, and studying such activity has been a high priority for HiRISE. Many examples of new deposits in gullies are now known. -
5.
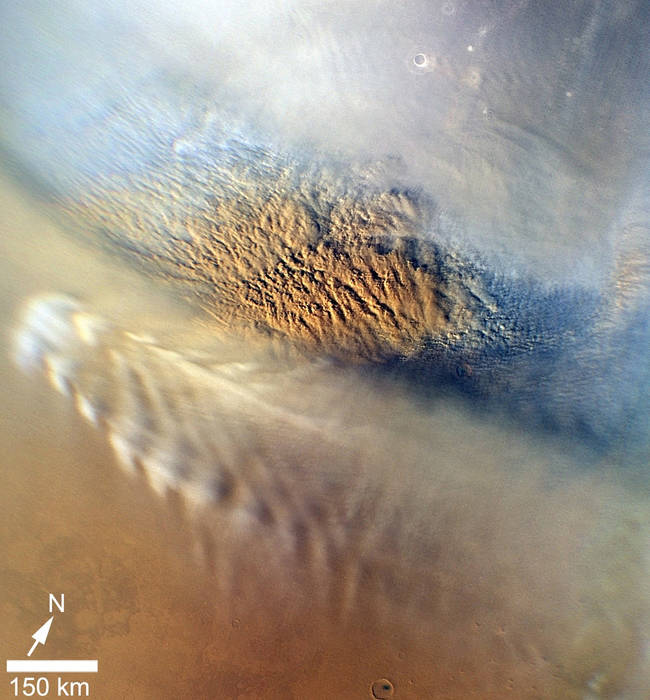 This close-up image of a dust storm on Mars was acquired by the Mars Color Imager instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on Nov. 7, 2007, around 3 p.m. local time on Mars. Scientists working with NASA's Curiosity rover, which is set to land on Mars on Aug. 5 PDT Aug. 6 EDT, are monitoring Mars each day for similar small storms that could either drift over the landing site or stir up dust that moves as haze over the site.
This close-up image of a dust storm on Mars was acquired by the Mars Color Imager instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on Nov. 7, 2007, around 3 p.m. local time on Mars. Scientists working with NASA's Curiosity rover, which is set to land on Mars on Aug. 5 PDT Aug. 6 EDT, are monitoring Mars each day for similar small storms that could either drift over the landing site or stir up dust that moves as haze over the site. -
6.
 A valley in Elysium region volcanic rise.
A valley in Elysium region volcanic rise. -
7.
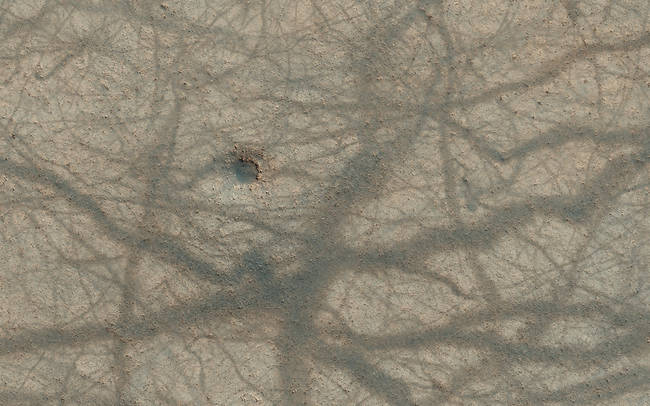 A small impact crater, pitted knobs, and a criss-cross mesh of dust devil trails across the martian surface.
A small impact crater, pitted knobs, and a criss-cross mesh of dust devil trails across the martian surface. -
8.
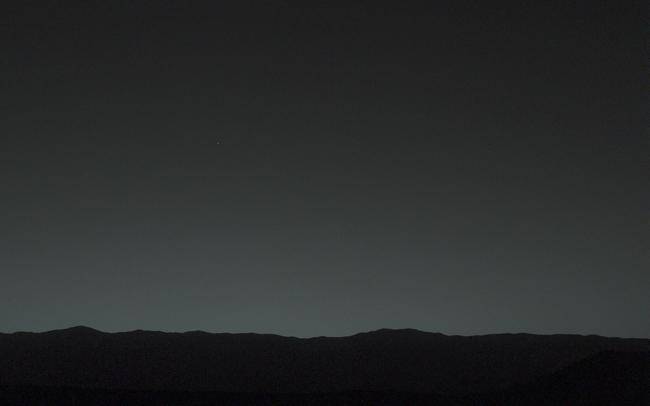 You are here! As an Evening Star in the Martian SkyThis evening-sky view taken by NASAs Mars rover Curiosity shows the Earth and Earths moon as seen on Jan. 31, 2014, or Sol 529 shortly after sunset at the Dingo Gap inside Gale Crater.
You are here! As an Evening Star in the Martian SkyThis evening-sky view taken by NASAs Mars rover Curiosity shows the Earth and Earths moon as seen on Jan. 31, 2014, or Sol 529 shortly after sunset at the Dingo Gap inside Gale Crater. -
9.
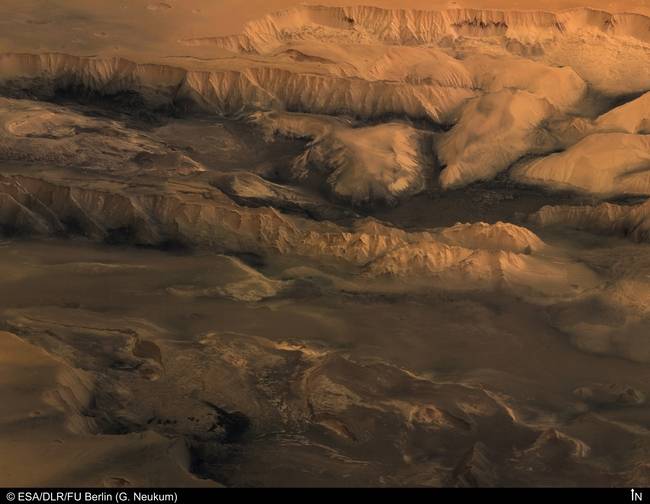 Valles Marineris Latin for Mariner Valleys, named after the Mariner 9 Mars orbiter of 197172 which discovered it is a system of canyons that runs along the Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than 4,000 km 2,500 mi long, 200 km 120 mi wide and up to 7 km 23,000 ft deep,
Valles Marineris Latin for Mariner Valleys, named after the Mariner 9 Mars orbiter of 197172 which discovered it is a system of canyons that runs along the Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than 4,000 km 2,500 mi long, 200 km 120 mi wide and up to 7 km 23,000 ft deep, -
10.
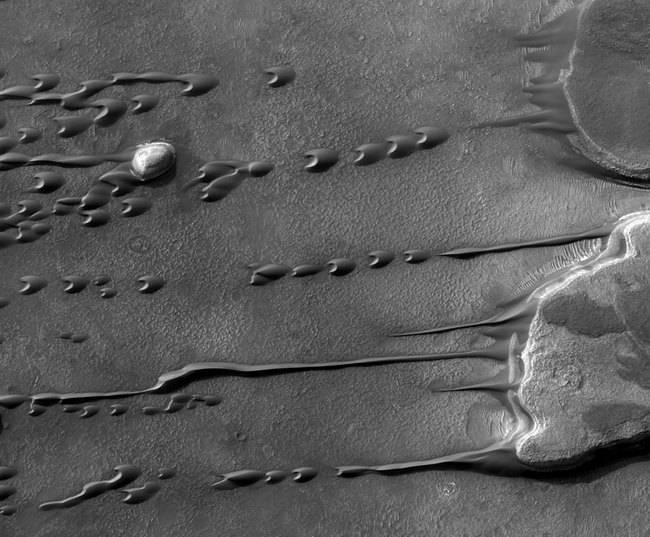 Crazy dune patterns. Its another HiRISE camera image, taken from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2009 when planetary scientists were beginning to glimpse the truly dynamic quality of the dunes but still werent positive how widespread dune movement is on Mars.
Crazy dune patterns. Its another HiRISE camera image, taken from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2009 when planetary scientists were beginning to glimpse the truly dynamic quality of the dunes but still werent positive how widespread dune movement is on Mars. -
11.
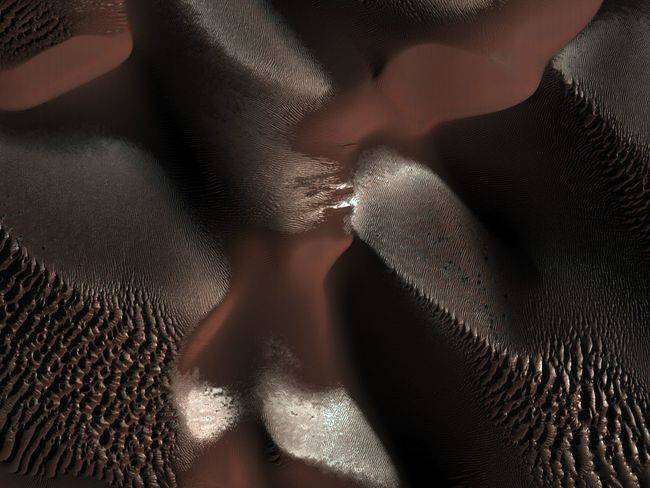 Dunes within a crater on Mars are visible in this image. This crater is located in the Southern hemisphere where it was winter at the time this image was taken.
Dunes within a crater on Mars are visible in this image. This crater is located in the Southern hemisphere where it was winter at the time this image was taken. -
12.
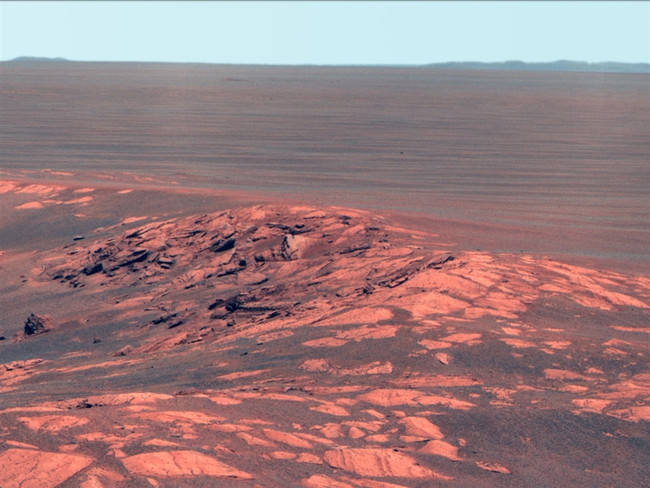 Desert in every direction.
Desert in every direction. -
13.
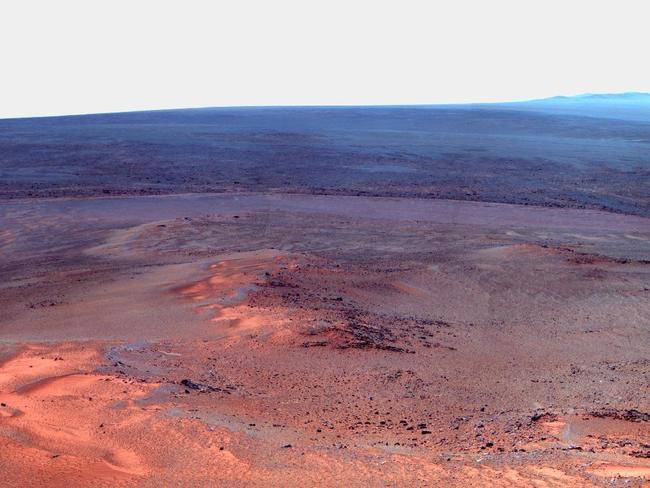 Opportunity's Panoramic Camera Pancam took the component images as part of full-circle view being assembled from Greeley Haven.
Opportunity's Panoramic Camera Pancam took the component images as part of full-circle view being assembled from Greeley Haven. -
14.
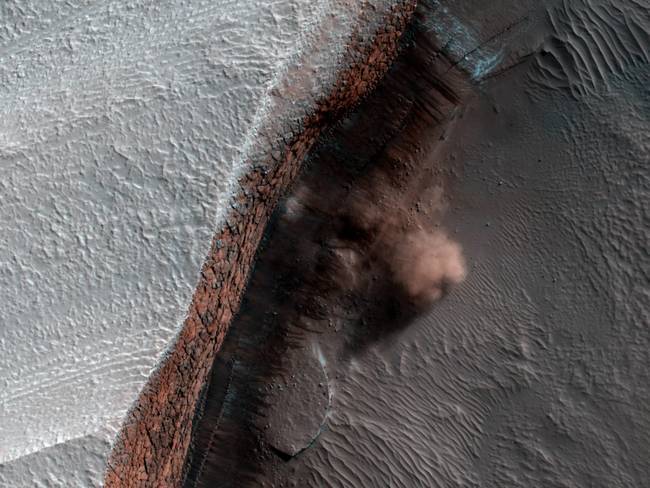 A NASA spacecraft in orbit around Mars has taken the first ever image of active avalanches near the Red Planet's north pole.
A NASA spacecraft in orbit around Mars has taken the first ever image of active avalanches near the Red Planet's north pole. -
15.
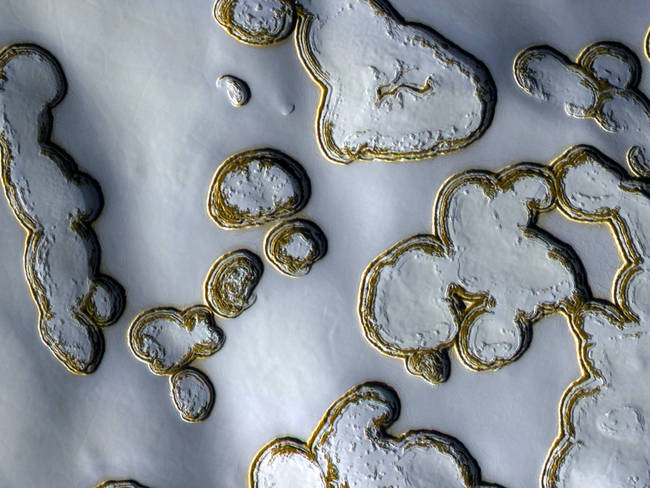 Planum Australe Latin: "the southern plain" is the southern polar plain on Mars. It extends southward of roughly 75S and is centered at 83.9S 160.0E. The geology of this region was to be explored by the failed NASA mission Mars Polar Lander, which lost contact on entry into the Martian atmosphere.
Planum Australe Latin: "the southern plain" is the southern polar plain on Mars. It extends southward of roughly 75S and is centered at 83.9S 160.0E. The geology of this region was to be explored by the failed NASA mission Mars Polar Lander, which lost contact on entry into the Martian atmosphere. -
16.
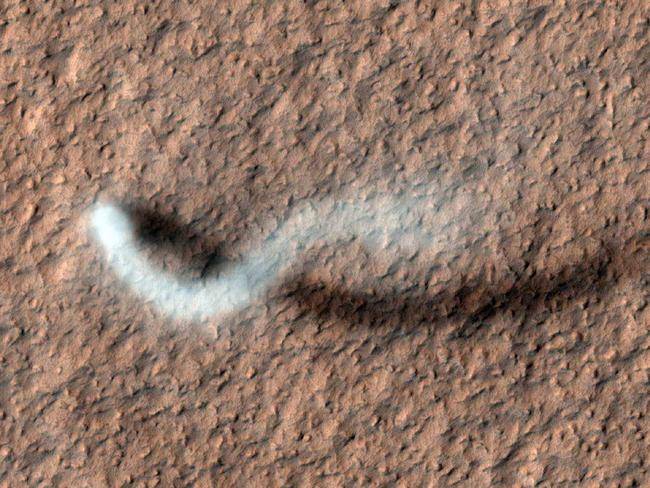 Mission members monitoring the Spirit rover on Mars reported on March 12, 2005, that a lucky encounter with a dust devil had cleaned the solar panels of that robot. Power levels dramatically increased and daily science work was anticipated to be expanded.20 A similar phenomenon solar panels mysteriously cleaned of accumulated dust had previously been observed with the Opportunity rover, and dust devils had also been suspected as the cause.
Mission members monitoring the Spirit rover on Mars reported on March 12, 2005, that a lucky encounter with a dust devil had cleaned the solar panels of that robot. Power levels dramatically increased and daily science work was anticipated to be expanded.20 A similar phenomenon solar panels mysteriously cleaned of accumulated dust had previously been observed with the Opportunity rover, and dust devils had also been suspected as the cause. -
17.
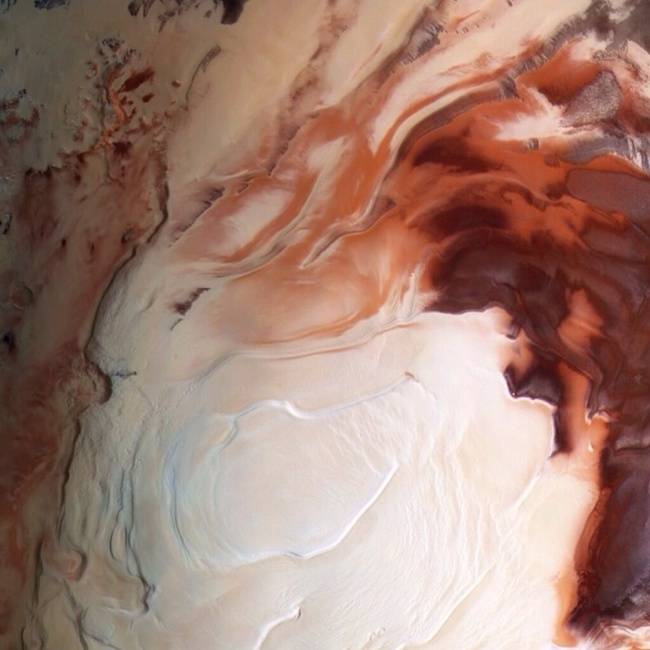 Mars' south pole.
Mars' south pole. -
18.
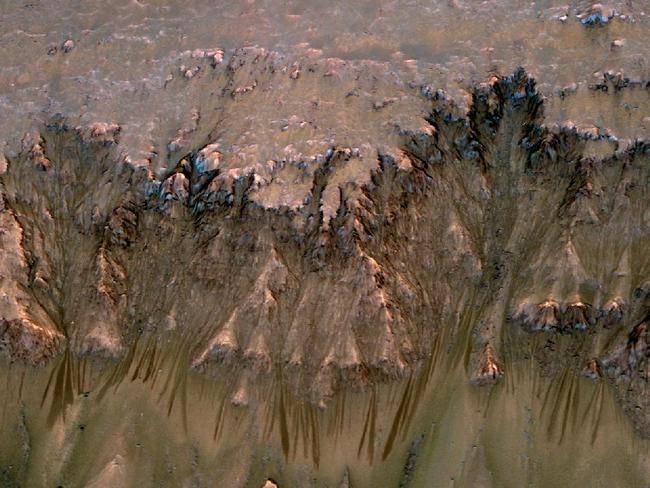 NASA spacecraft orbiting Mars have returned clues for understanding seasonal features that are the strongest indication of possible liquid water that may exist today on the Red Planet.
NASA spacecraft orbiting Mars have returned clues for understanding seasonal features that are the strongest indication of possible liquid water that may exist today on the Red Planet. -
19.
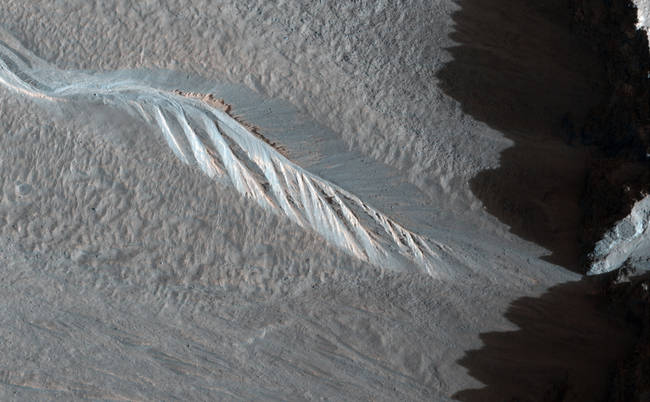 Large Shadows and Huge Dunes.
Large Shadows and Huge Dunes. -
20.
 Glaciation at the Eastern Hellas Margin.
Glaciation at the Eastern Hellas Margin. -
21.
 Defrosting dunes in the north. In northern winter a seasonal polar cap composed of carbon dioxide ice dry ice forms in the north polar region. This cap covers a vast sea of dunes at high northern latitudes. In the spring the ice sublimates evaporates directly from ice to gas and this active process loosens and moves tiny dust particles. More, or see location on Google Mars.
Defrosting dunes in the north. In northern winter a seasonal polar cap composed of carbon dioxide ice dry ice forms in the north polar region. This cap covers a vast sea of dunes at high northern latitudes. In the spring the ice sublimates evaporates directly from ice to gas and this active process loosens and moves tiny dust particles. More, or see location on Google Mars. -
22.
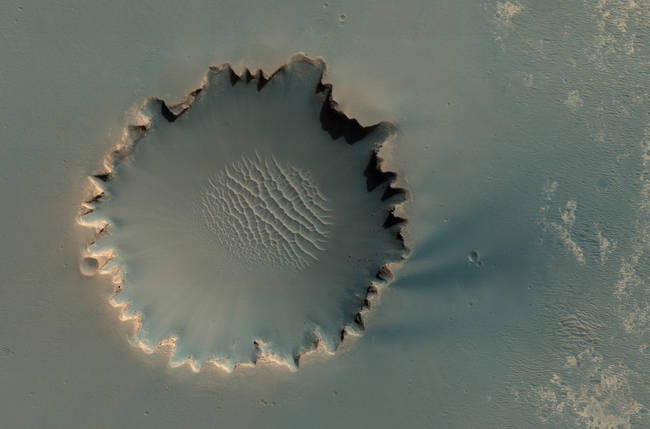 Victoria Crater at Meridiani Planum. The crater is approximately 800 meters about half a mile in diameter. Layered sedimentary rocks are exposed along the inner wall of the crater, and boulders that have fallen from the crater wall are visible on the crater floor. NASA's Mars rover Opportunity explored this crater and its walls in 2006. More, or see location on Google Mars.
Victoria Crater at Meridiani Planum. The crater is approximately 800 meters about half a mile in diameter. Layered sedimentary rocks are exposed along the inner wall of the crater, and boulders that have fallen from the crater wall are visible on the crater floor. NASA's Mars rover Opportunity explored this crater and its walls in 2006. More, or see location on Google Mars. -
23.
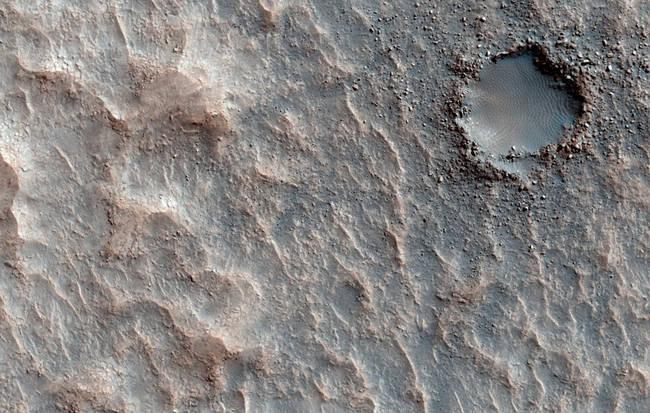 A small impact crater, surrounded by ejecta, is filled in with rippled sand on the floor of Ritchey Crater. More, or see location on Google Mars.
A small impact crater, surrounded by ejecta, is filled in with rippled sand on the floor of Ritchey Crater. More, or see location on Google Mars. -
24.
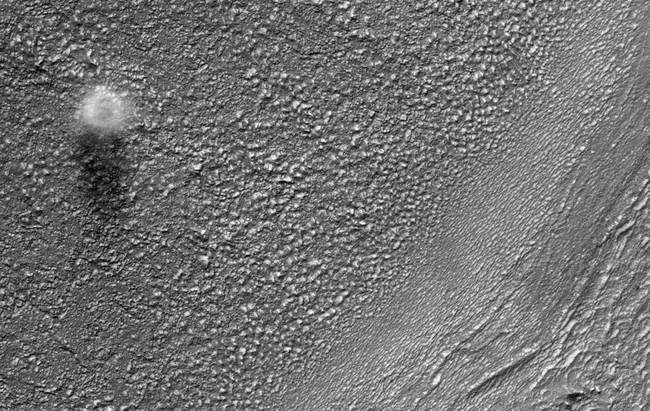 HiRISE catches a dust devil blowing across the Martian surface east of the Hellas impact basin and south of Reull Vallis. The diameter of this dust devil is about 200 meters, but at the surface it is probably much smaller. Based on the length of the shadow in this image, the dust devil is on the order of 500 meters tall.
HiRISE catches a dust devil blowing across the Martian surface east of the Hellas impact basin and south of Reull Vallis. The diameter of this dust devil is about 200 meters, but at the surface it is probably much smaller. Based on the length of the shadow in this image, the dust devil is on the order of 500 meters tall. -
25.
 The south polar region of Mars is covered every year by a layer of carbon dioxide ice. In a region called the "cryptic terrain," the ice is translucent and sunlight can penetrate through the ice to warm the surface below. The ice layer sublimates evaporates from the bottom. The dark fans of dust seen in this image come from the surface below the layer of ice, carried to the top by gas venting from below. The translucent ice is "visible" by virtue of the effect it has on the tone of the surface below, which would otherwise have the same color and reflectivity as the fans. Bright streaks in this image are fresh frost.
The south polar region of Mars is covered every year by a layer of carbon dioxide ice. In a region called the "cryptic terrain," the ice is translucent and sunlight can penetrate through the ice to warm the surface below. The ice layer sublimates evaporates from the bottom. The dark fans of dust seen in this image come from the surface below the layer of ice, carried to the top by gas venting from below. The translucent ice is "visible" by virtue of the effect it has on the tone of the surface below, which would otherwise have the same color and reflectivity as the fans. Bright streaks in this image are fresh frost. -
26.
 Scalloped sand dunes in the southern hemisphere of mars, displaying seasonal frost on the south-facing slopes, which highlights some of the regular patterns, as the frost forms only on parts of the ripples.
Scalloped sand dunes in the southern hemisphere of mars, displaying seasonal frost on the south-facing slopes, which highlights some of the regular patterns, as the frost forms only on parts of the ripples. -
27.
 An eroded crater in a larger plain with a scalloped appearance near Pavonis Mons.
An eroded crater in a larger plain with a scalloped appearance near Pavonis Mons. -
28.
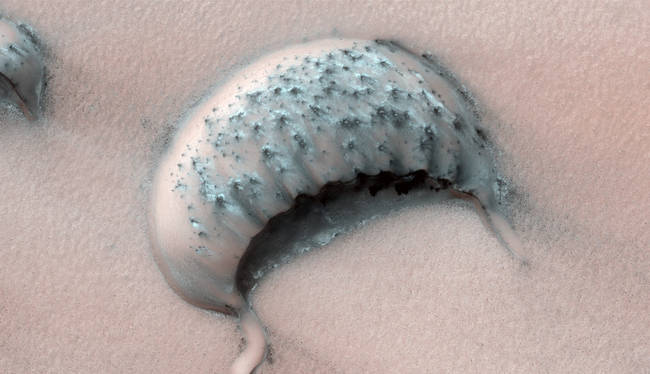 A large barchan crescent-shaped dune, in a region where some dunes have been observed shrinking over several years.
A large barchan crescent-shaped dune, in a region where some dunes have been observed shrinking over several years. -
29.
 A person does not cease to search for life on our nearest planet. And even when he is absolutely sure to make sure that the solar system we are alone, he will begin to look for signs of extinct life on Mars. And this quest, after the analysis of the soil, it is useful to start with the atmosphere of the Red Planet.
A person does not cease to search for life on our nearest planet. And even when he is absolutely sure to make sure that the solar system we are alone, he will begin to look for signs of extinct life on Mars. And this quest, after the analysis of the soil, it is useful to start with the atmosphere of the Red Planet.
- REPLAY GALLERY
-

- Background Worthy Mars Photos
Gale is a crater on Mars near the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle at 5.4S 137.8E.2 It is 154 km 96 mi in diameter1 and estimated to be about 3.5-3.8 billion years old.
29/29
1/29





4 Comments