Greatest Minds and Philosophers of the World
El_Socrates
Published
10/18/2013
Just a small selection of very influential people to grace our planet. Enjoy
- List View
- Player View
- Grid View
Advertisement
-
1.
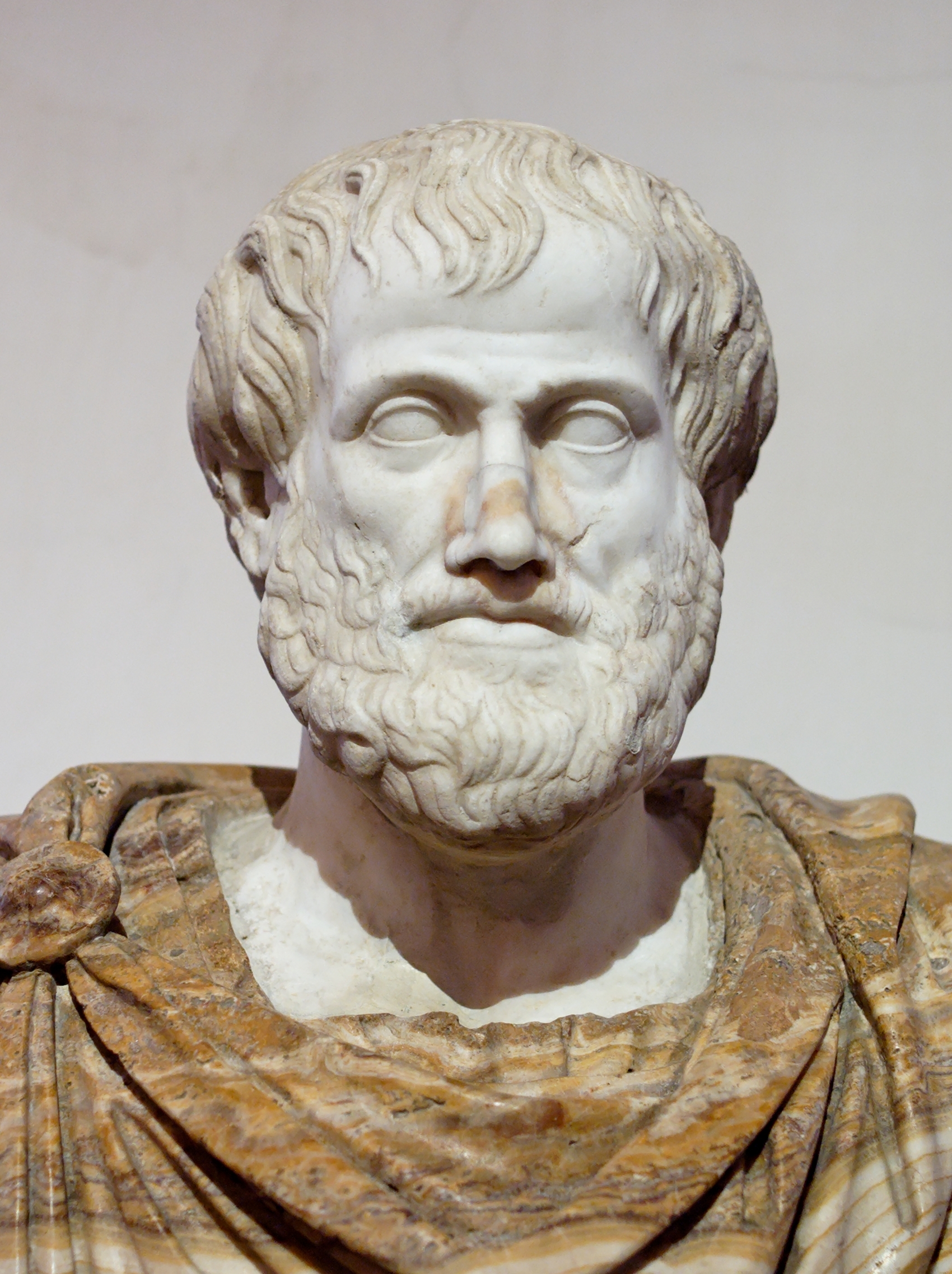 Aristotle 384 BC to 322 BC was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology
Aristotle 384 BC to 322 BC was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology -
2.
 Plato 427 BC to 347 BC was a philosopher in Classical Greece. He was also a mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the foundations of Western philosophy and science
Plato 427 BC to 347 BC was a philosopher in Classical Greece. He was also a mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the foundations of Western philosophy and science -
3.
 Pythagoras 570 BC to c. 495 BC was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him
Pythagoras 570 BC to c. 495 BC was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him -
4.
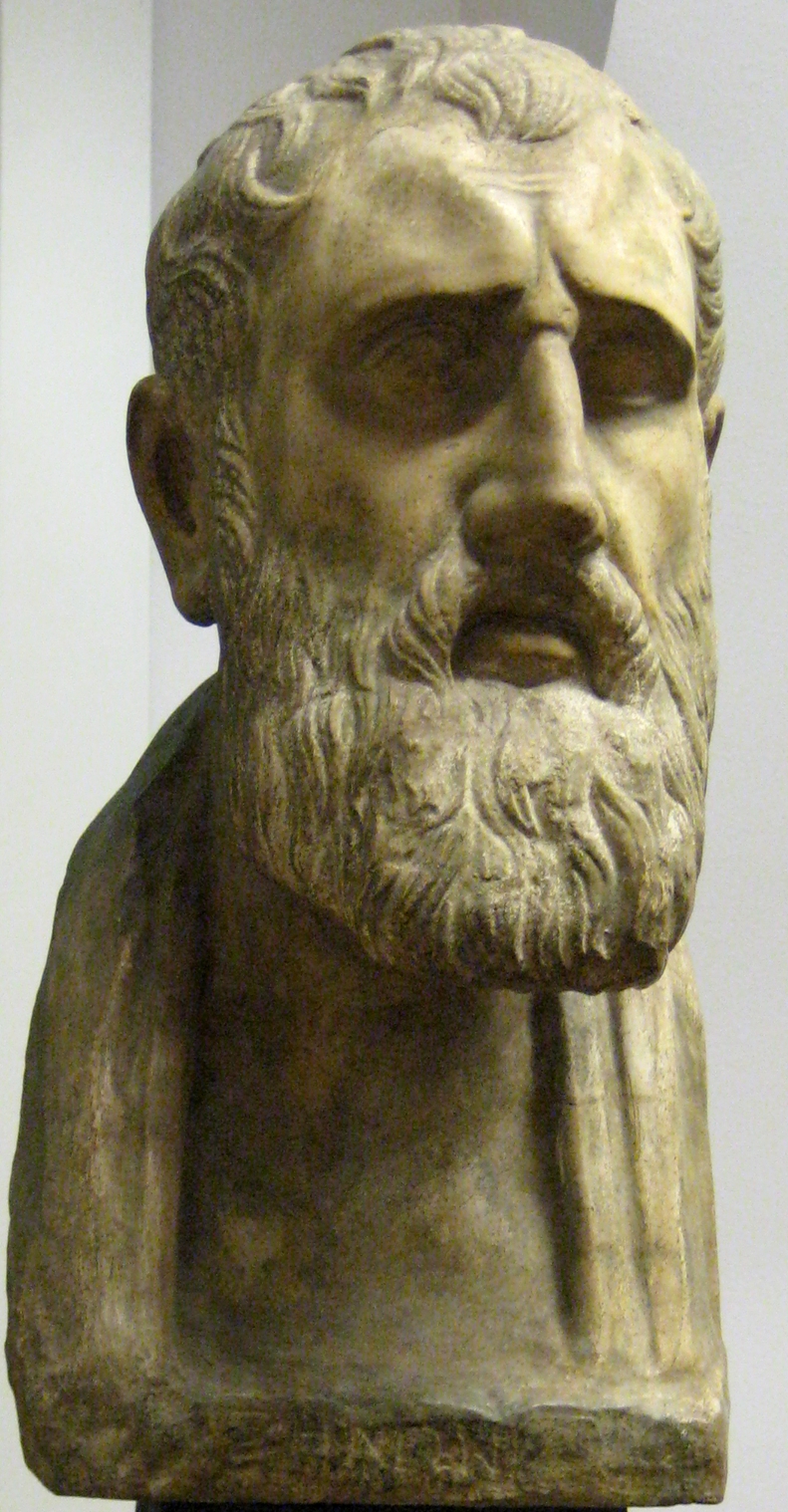 Zeno of Elea 490 BC to ca. 430 BC was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher of southern Italy and a member of the Eleatic School founded by Parmenides. Aristotle called him the inventor of the dialectic
Zeno of Elea 490 BC to ca. 430 BC was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher of southern Italy and a member of the Eleatic School founded by Parmenides. Aristotle called him the inventor of the dialectic -
5.
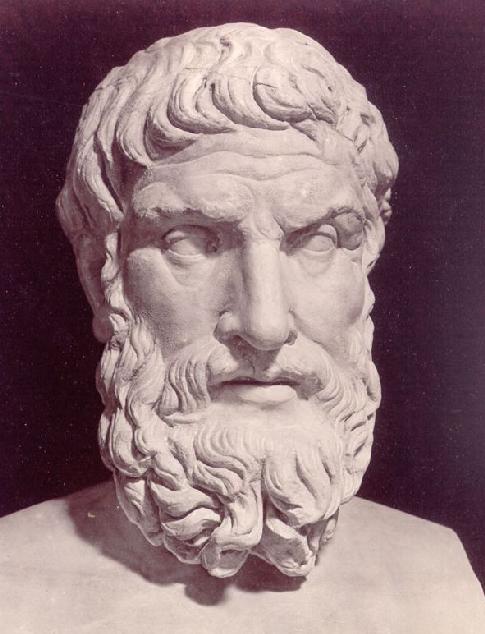 Epicurus 341 BC to 270 BC was an ancient Greek philosopher as well as the founder of the school of philosophy called Epicureanism. Only a few fragments and letters of Epicurus's 300 written works remain. Much of what is known about Epicurean philosophy derives from later followers and commentators
Epicurus 341 BC to 270 BC was an ancient Greek philosopher as well as the founder of the school of philosophy called Epicureanism. Only a few fragments and letters of Epicurus's 300 written works remain. Much of what is known about Epicurean philosophy derives from later followers and commentators -
6.
 Avicenna c. 980 to June 1037 was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived. In particular, 150 of his surviving treatises concentrate on philosophy and 40 of them concentrate on medicine
Avicenna c. 980 to June 1037 was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived. In particular, 150 of his surviving treatises concentrate on philosophy and 40 of them concentrate on medicine -
7.
 Leonardo Da Vinci April 15, 1452 to May 2, 1519 was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist, and writer. His genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance humanist ideal
Leonardo Da Vinci April 15, 1452 to May 2, 1519 was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist, and writer. His genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance humanist ideal -
8.
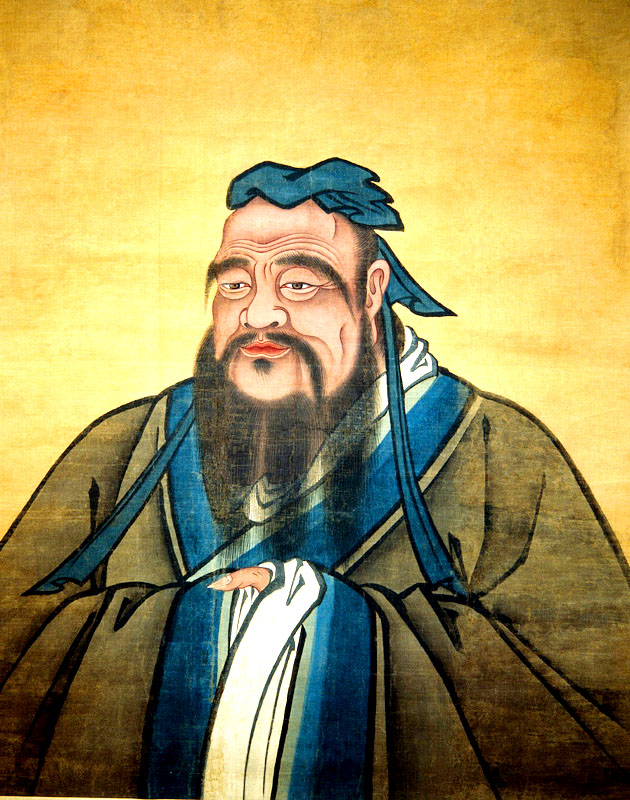 Confucius 551 to 479 BC was a Chinese teacher, editor, politician, and philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history
Confucius 551 to 479 BC was a Chinese teacher, editor, politician, and philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history -
9.
 Thomas Aquinas 28 January 1225 to 7 March 1274 Dominican friar and priest and an immensely influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism, within which he is also known as the "Doctor Angelicus", "Doctor Communis", and "Doctor Universalis Aquinas" is the demonym of Aquino, his home town
Thomas Aquinas 28 January 1225 to 7 March 1274 Dominican friar and priest and an immensely influential philosopher and theologian in the tradition of scholasticism, within which he is also known as the "Doctor Angelicus", "Doctor Communis", and "Doctor Universalis Aquinas" is the demonym of Aquino, his home town -
10.
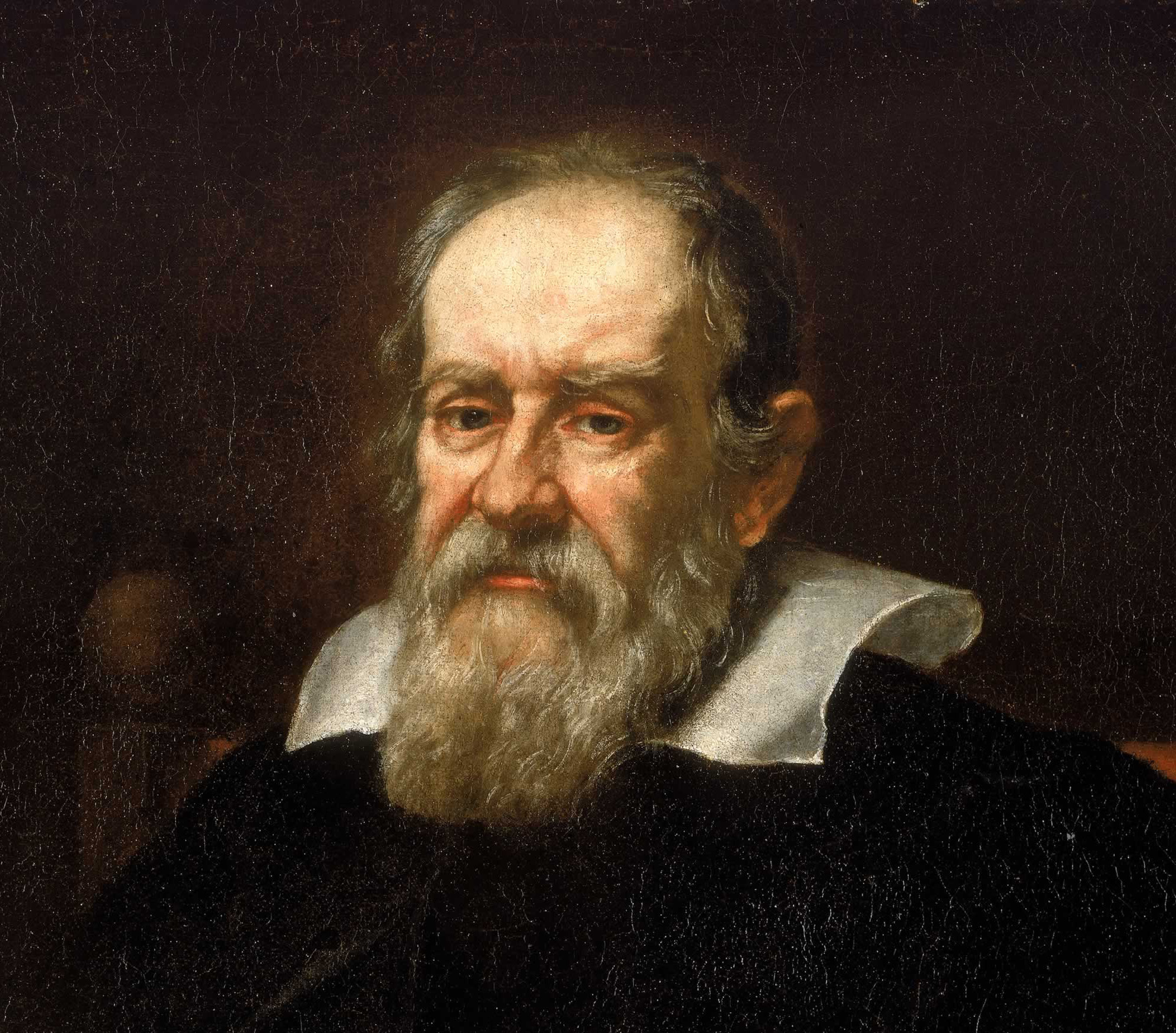 Galileo February 1564 to January 1642 was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism. Galileo has been called the "father of modern observational astronomy"
Galileo February 1564 to January 1642 was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism. Galileo has been called the "father of modern observational astronomy" -
11.
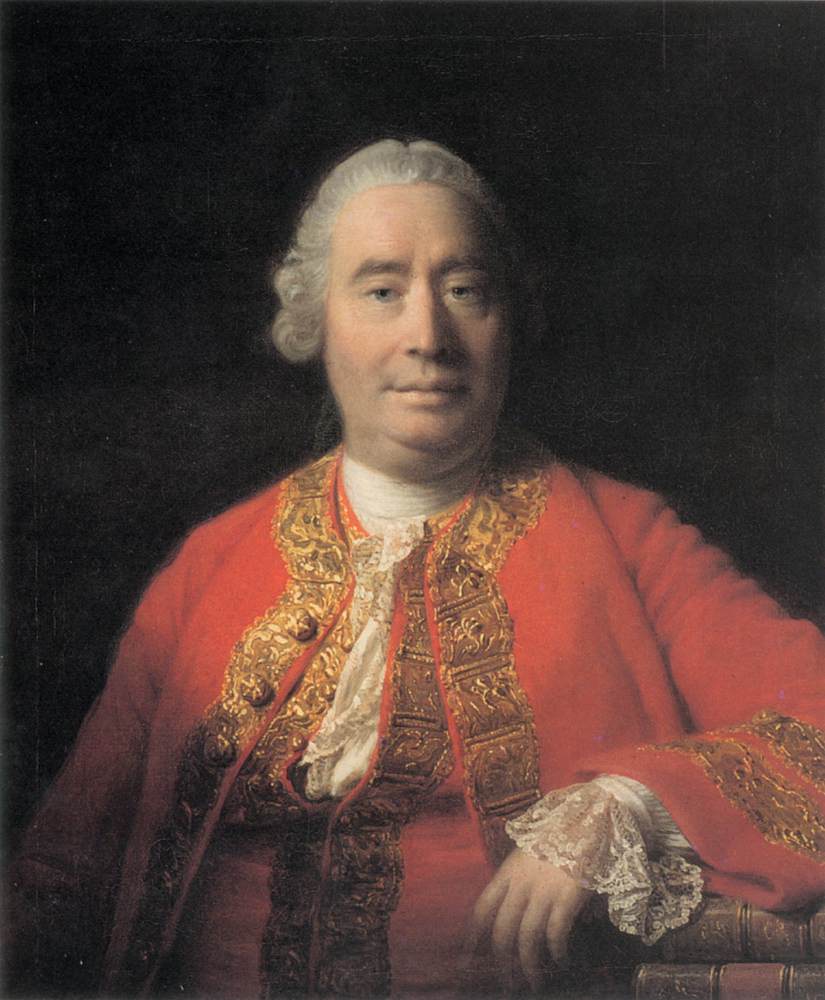 David Hume 1711 to August 1776 was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist known especially for his philosophical empiricism and skepticism. He was one of the most important figures in the history of Western philosophy and the Scottish Enlightenment
David Hume 1711 to August 1776 was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist known especially for his philosophical empiricism and skepticism. He was one of the most important figures in the history of Western philosophy and the Scottish Enlightenment -
12.
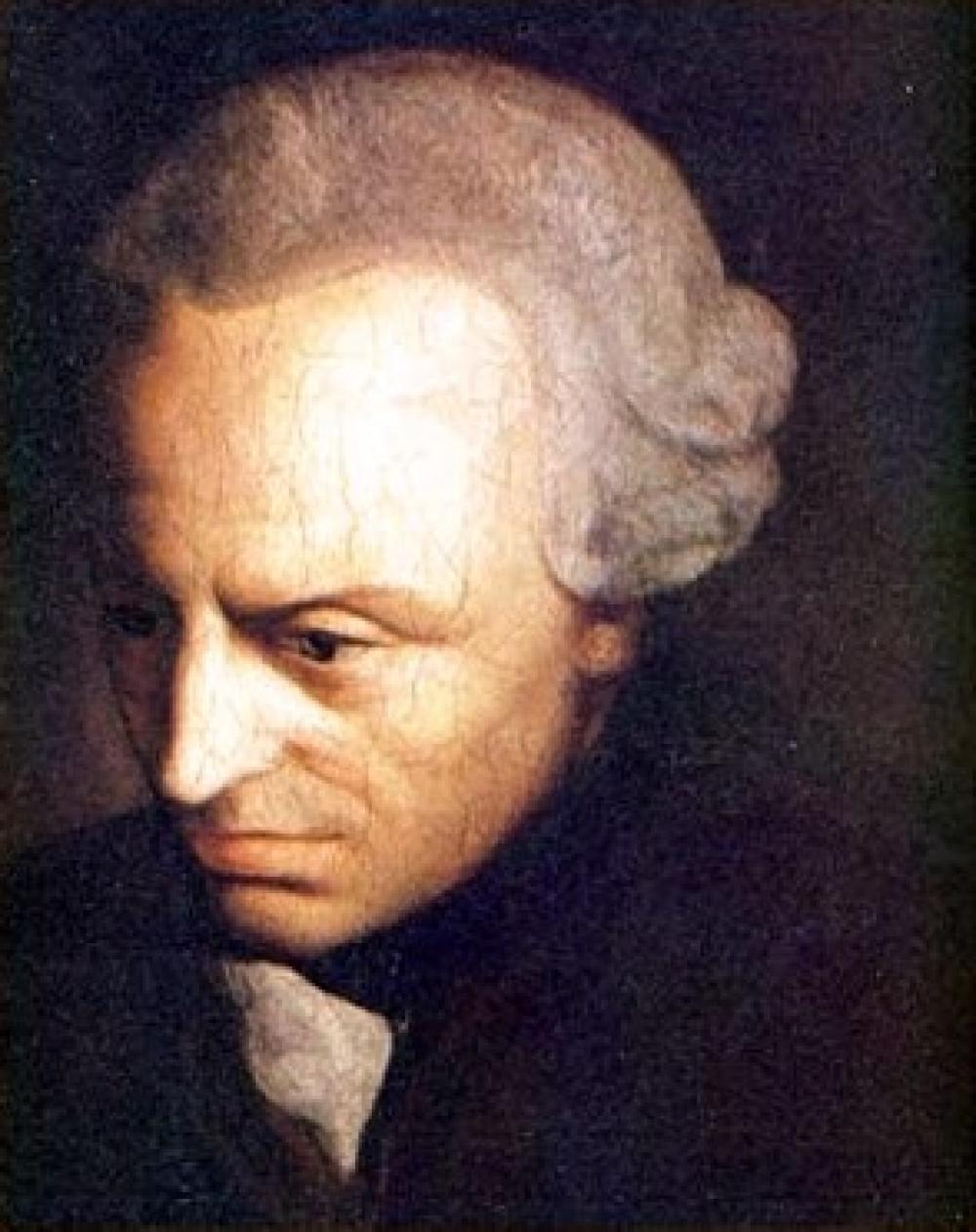 Immanuel Kant 1724 to February 1804 was a German philosopher who is widely considered to be a central figure of modern philosophy. He argued that human concepts and categories structure our view of the world and its laws, and that reason is the source of morality. His thought continues to hold a major influence in contemporary thought, especially in fields such as metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, political philosophy, and aesthetics
Immanuel Kant 1724 to February 1804 was a German philosopher who is widely considered to be a central figure of modern philosophy. He argued that human concepts and categories structure our view of the world and its laws, and that reason is the source of morality. His thought continues to hold a major influence in contemporary thought, especially in fields such as metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, political philosophy, and aesthetics -
13.
 Laoizi "Lao Tzu" 6th century BC was a philosopher of ancient China, best known as the author of the Tao Te Ching often simply referred to as Laozi. His association with the To T Ch299ng has led him to be traditionally considered the founder of philosophical Taoism pronounced as "Daoism". He is also revered as a deity in most religious forms of Taoist philosophy, which often refers to Laozi as Taishang Laojun, or "One of the Three Pure Ones"
Laoizi "Lao Tzu" 6th century BC was a philosopher of ancient China, best known as the author of the Tao Te Ching often simply referred to as Laozi. His association with the To T Ch299ng has led him to be traditionally considered the founder of philosophical Taoism pronounced as "Daoism". He is also revered as a deity in most religious forms of Taoist philosophy, which often refers to Laozi as Taishang Laojun, or "One of the Three Pure Ones" -
14.
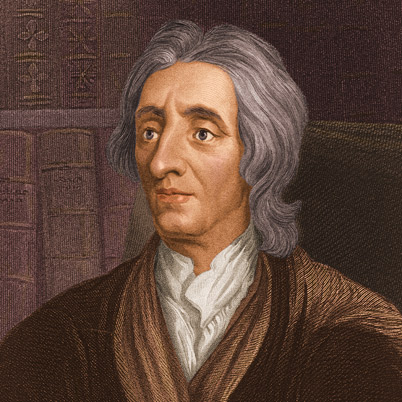 John Locke August 1632 to October 1704 widely known as the Father of Classical Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social contract theory
John Locke August 1632 to October 1704 widely known as the Father of Classical Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social contract theory -
15.
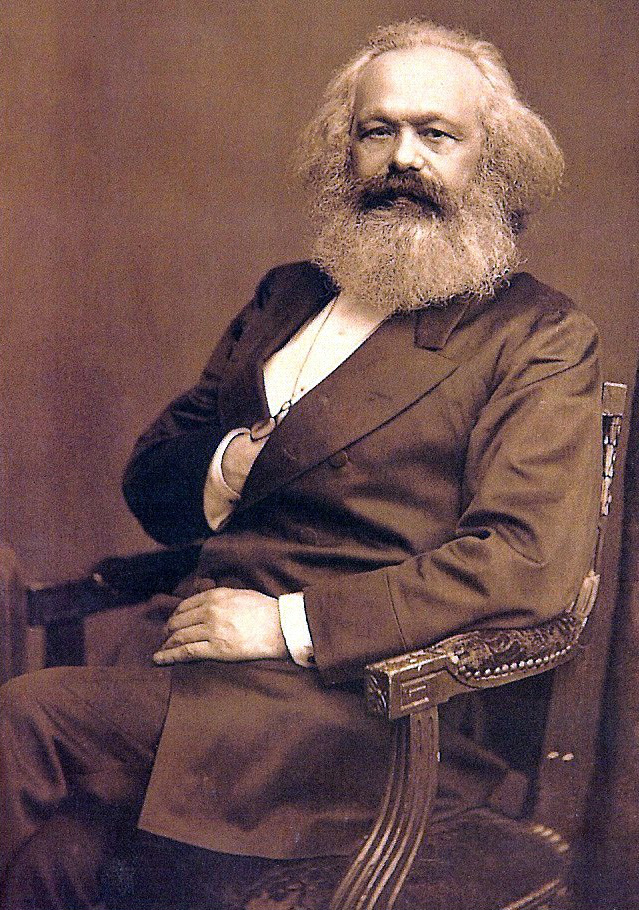 Karl Marx May 1818 to March 1883 was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. Marx's work in economics laid the basis for the current understanding of labour and its relation to capital, and has influenced much of subsequent economic thought. He published numerous books during his lifetime, the most notable being The Communist Manifesto 1848 and Das Kapital 18671894
Karl Marx May 1818 to March 1883 was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. Marx's work in economics laid the basis for the current understanding of labour and its relation to capital, and has influenced much of subsequent economic thought. He published numerous books during his lifetime, the most notable being The Communist Manifesto 1848 and Das Kapital 18671894 -
16.
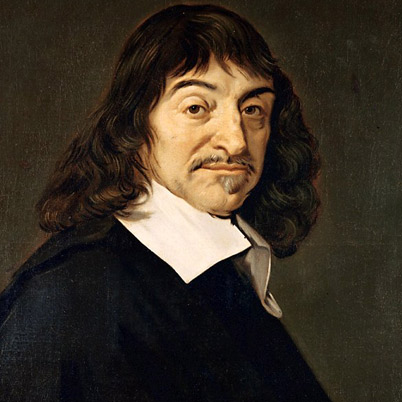 Rene Descartes March 1596 to February 1650 was a French philosopher, mathematician, and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the 'Father of Modern Philosophy', and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings,which are studied closely to this day. In particular, his Meditations on First Philosophy continues to be a standard text at most university philosophy departments
Rene Descartes March 1596 to February 1650 was a French philosopher, mathematician, and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the 'Father of Modern Philosophy', and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings,which are studied closely to this day. In particular, his Meditations on First Philosophy continues to be a standard text at most university philosophy departments -
17.
 Friedrich Nietzsche October 1844 to August 1900 was a German philologist, philosopher, cultural critic, poet and composer. He wrote several critical texts on religion, morality, contemporary culture, philosophy and science, displaying a fondness for metaphor, irony and aphorism
Friedrich Nietzsche October 1844 to August 1900 was a German philologist, philosopher, cultural critic, poet and composer. He wrote several critical texts on religion, morality, contemporary culture, philosophy and science, displaying a fondness for metaphor, irony and aphorism -
18.
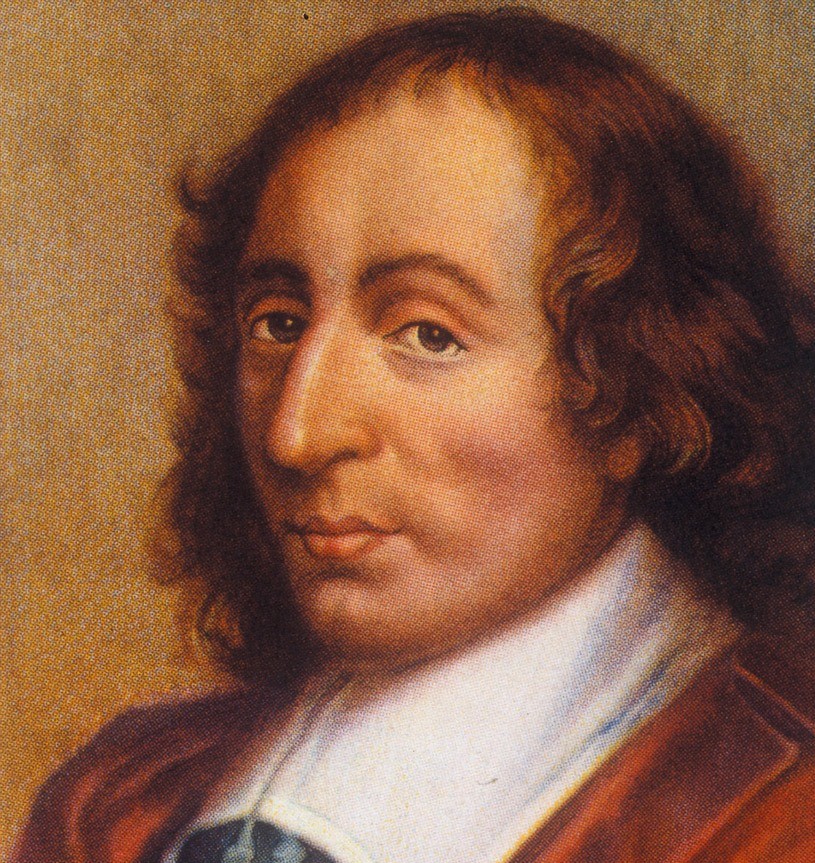 Blaise Pascal June 1623 to August 1662 was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer and Christian philosopher. He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earliest work was in the natural and applied sciences where he made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure and vacuum by generalizing the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal also wrote in defense of the scientific method
Blaise Pascal June 1623 to August 1662 was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer and Christian philosopher. He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earliest work was in the natural and applied sciences where he made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure and vacuum by generalizing the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal also wrote in defense of the scientific method -
19.
 Albert Einstein March 1879 to April 1955 was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics alongside quantum mechanics. While best known for his massenergy equivalence formula E mc2 which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation", he received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". The latter was pivotal in establishing quantum theory
Albert Einstein March 1879 to April 1955 was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics alongside quantum mechanics. While best known for his massenergy equivalence formula E mc2 which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation", he received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". The latter was pivotal in establishing quantum theory -
20.
 Jean Paiget August 1896 to September 1980 was a Swiss developmental psychologist and philosopher known for his epistemological studies with children. His theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology"
Jean Paiget August 1896 to September 1980 was a Swiss developmental psychologist and philosopher known for his epistemological studies with children. His theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology" -
21.
 Dalai Lama 1357 to 1419 The name is a combination of the Mongolian word dalai meaning "vast sea" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "guru, teacher, mentor"
Dalai Lama 1357 to 1419 The name is a combination of the Mongolian word dalai meaning "vast sea" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "guru, teacher, mentor" -
22.
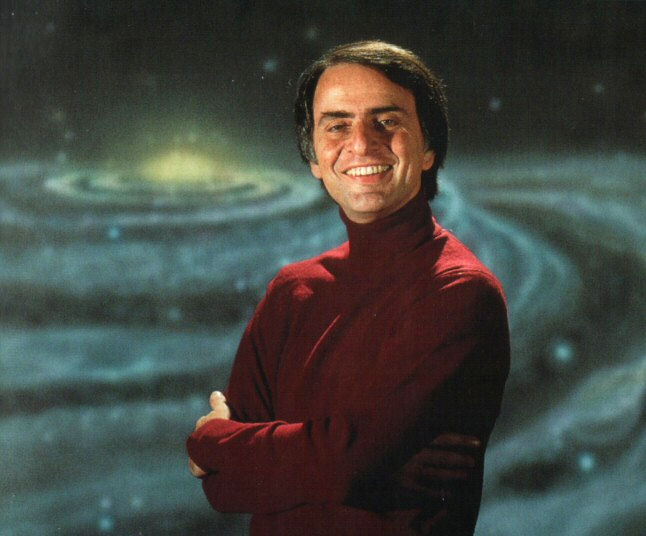 Carl Sagan 1934 to 1996 was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, author, science popularizer and science communicator in astronomy and natural sciences. He spent most of his career as a professor of astronomy at Cornell University where he directed the Laboratory for Planetary Studies. He published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books. He advocated scientific skeptical inquiry and the scientific method, pioneered exobiology and promoted the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
Carl Sagan 1934 to 1996 was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, author, science popularizer and science communicator in astronomy and natural sciences. He spent most of his career as a professor of astronomy at Cornell University where he directed the Laboratory for Planetary Studies. He published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books. He advocated scientific skeptical inquiry and the scientific method, pioneered exobiology and promoted the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence -
23.
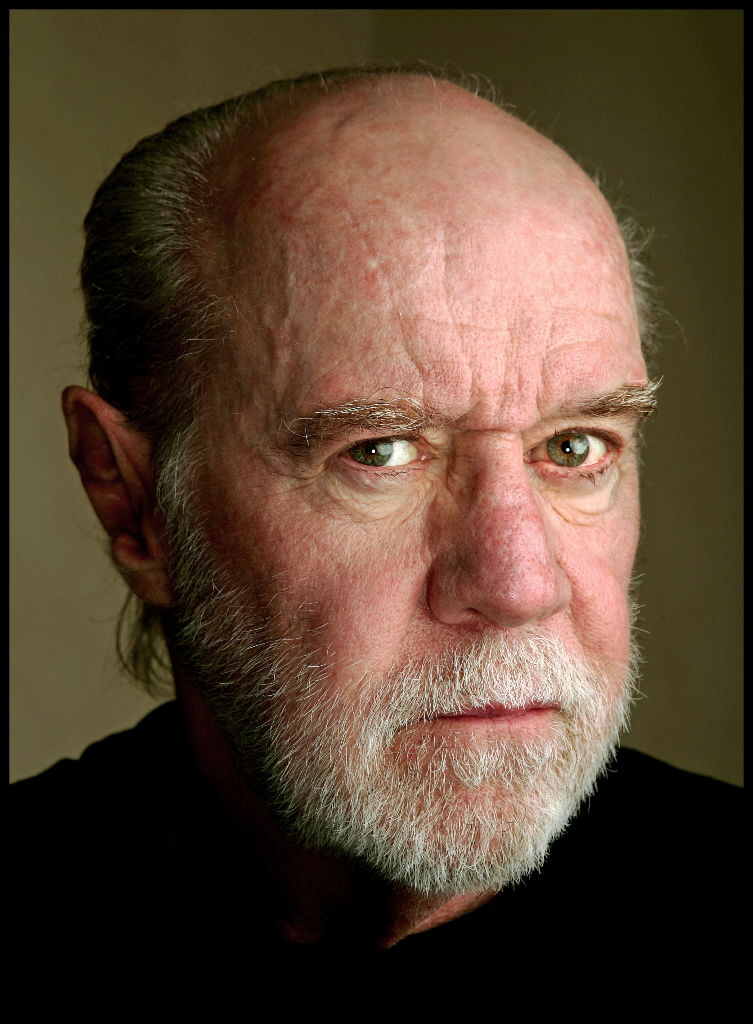 George Carlin 1937 to 2008 was an American stand-up comedian, social critic, philosopher, satirist, actor, and writerauthor who won five Grammy Awards for his comedy albums. Carlin was noted for his black humor as well as his thoughts on politics, the English language, psychology, religion, and various taboo subjects
George Carlin 1937 to 2008 was an American stand-up comedian, social critic, philosopher, satirist, actor, and writerauthor who won five Grammy Awards for his comedy albums. Carlin was noted for his black humor as well as his thoughts on politics, the English language, psychology, religion, and various taboo subjects
Aristotle 384 BC to 322 BC was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology
23/23
1/23








3 Comments